- A small degree of TR is present in the majority of normal individuals (like with PR).
- The most common cause of TR is secondary or functional regurgitation, due to annular dilatation from either right atrial or RV enlargement
- The most common cause of primary TR is myxomatous degeneration
- Patients with TR commonly have coexisting conditions including HF, pulmonary hypertension, chronic lung disease, AFib, and cardiovascular implantable electronic devices
- Secondary TR (80%) is much more common than primary TR (5-10%). The remainder are related to CIED leads (10-15%). 1
- ⚠️ When tricuspid regurgitation (TR) is severe, estimation of PASP derived from the tricuspid regurgitant jet and an estimate of right atrial pressure method may be less accurate.
- Although some degree of prolapse is common for the nonplanar TV, actual “TV prolapse” is typically reserved for excessive billowing into the right atrium associated with redundancy of the tricuspid leaflets.
- This abnormality is seen in 20% of patients with concomitant MVP
- Flail TV leaflets
- ⚠️ Flail leaflets are not typically associated with myxomatous TV disease but rather with closed chest trauma or RV endomyocardial biopsy
- Pacemaker leads can result in significant TR by interfering with closure of the TV but rarely cause a flail leaflet or a perforation of the leaflet
TR Phenotypes
1 proposed TR phenotypes include 4 classes: atrial secondary TR (A-STR), ventricular secondary TR (V-STR), CIED-related TR, and primary TR with primary prolapse and primary right heart disease as subgroups
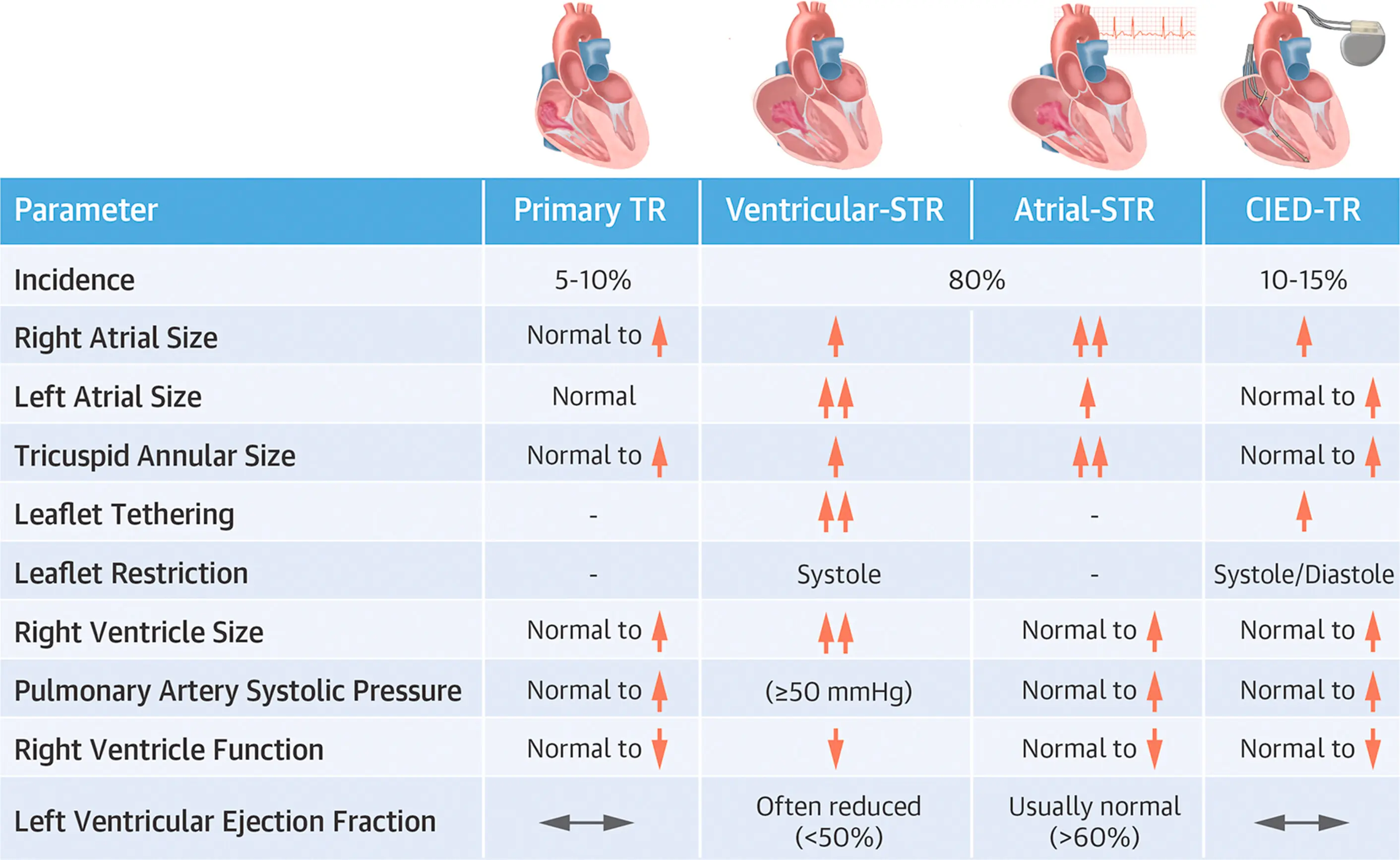
Primary TR
- Primary TR is defined as a defect of the valvular apparatus in the leaflets and chordae caused by either myxomatous prolapse, congenital heart disease, rheumatic heart disease, infective endocarditis, carcinoid heart disease, infiltrative valve disease, or iatrogenic mechanisms including RV biopsy. 1
Secondary TR
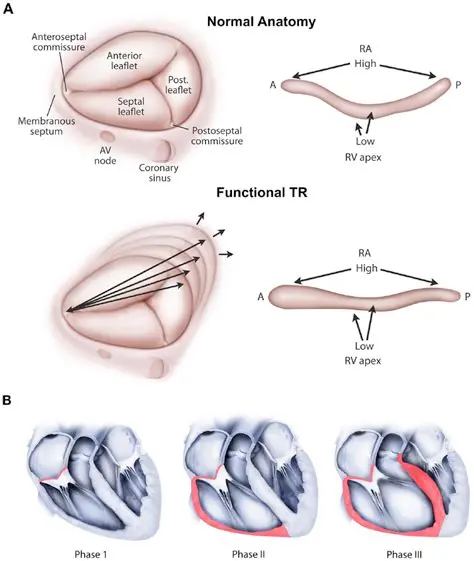
- Secondary TR, aka functional TR, is characterized by normal leaflets that are separated, tented, or tethered through a variety of mechanisms including annular dilatation, and RV enlargement and dysfunction. 1
- Specific etiologies of secondary TR include left ventricular systolic dysfunction, RV dysfunction from any cause, chronic lung disease, PH, myocardial disease, and AF. 1
Echo
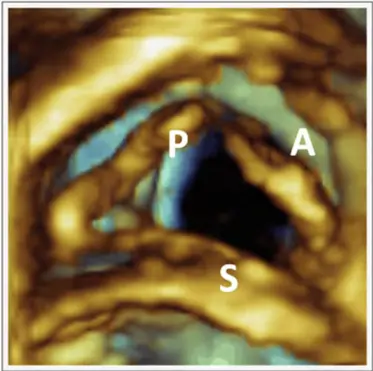
- On short axis (SAX), the leaflet adjacent to the aorta is either the septal or anterior leaflet, and the leaflet adjacent to the RV free wall is usually the posterior leaflet
- In the apical four-chamber (A4C) view, there is more certainty, with the anterior leaflet on the free wall and the septal leaflet adjacent to the septum.
- Three-dimensional echo provides unique en face views of the TV that enable simultaneous visualization of all three leaflets and the entire annulus
- Clues 🗝️
- The RV is usually dilated in the presence of hemodynamically significant TR.
- Significant chronic TR also causes enlargement of the RA and IVC.
- Septal Flattening
- The position of the septum produces a D-shaped LV predominantly in diastole (RV volume overload pattern).2
- When TR is due to pulmonary hypertension, septal flattening is present throughout the cardiac cycle, reflecting the diastolic and systolic overload of the RV (RV pressure overload pattern).2
- Parameters that signify severe TR are:
- VCW ≥0.7 cm
- PISA radius >0.9 cm
- EROA of ≥0.40 cm2
- RVol ≥45 mL
- Significant annular dilatation is defined by an end-diastolic diameter ≥40 mm or >21 mm/m2 in the four-chamber TTE view and is the main imaging criterion used to indicate severe TR in the current the ACC/AHA guidelines.2
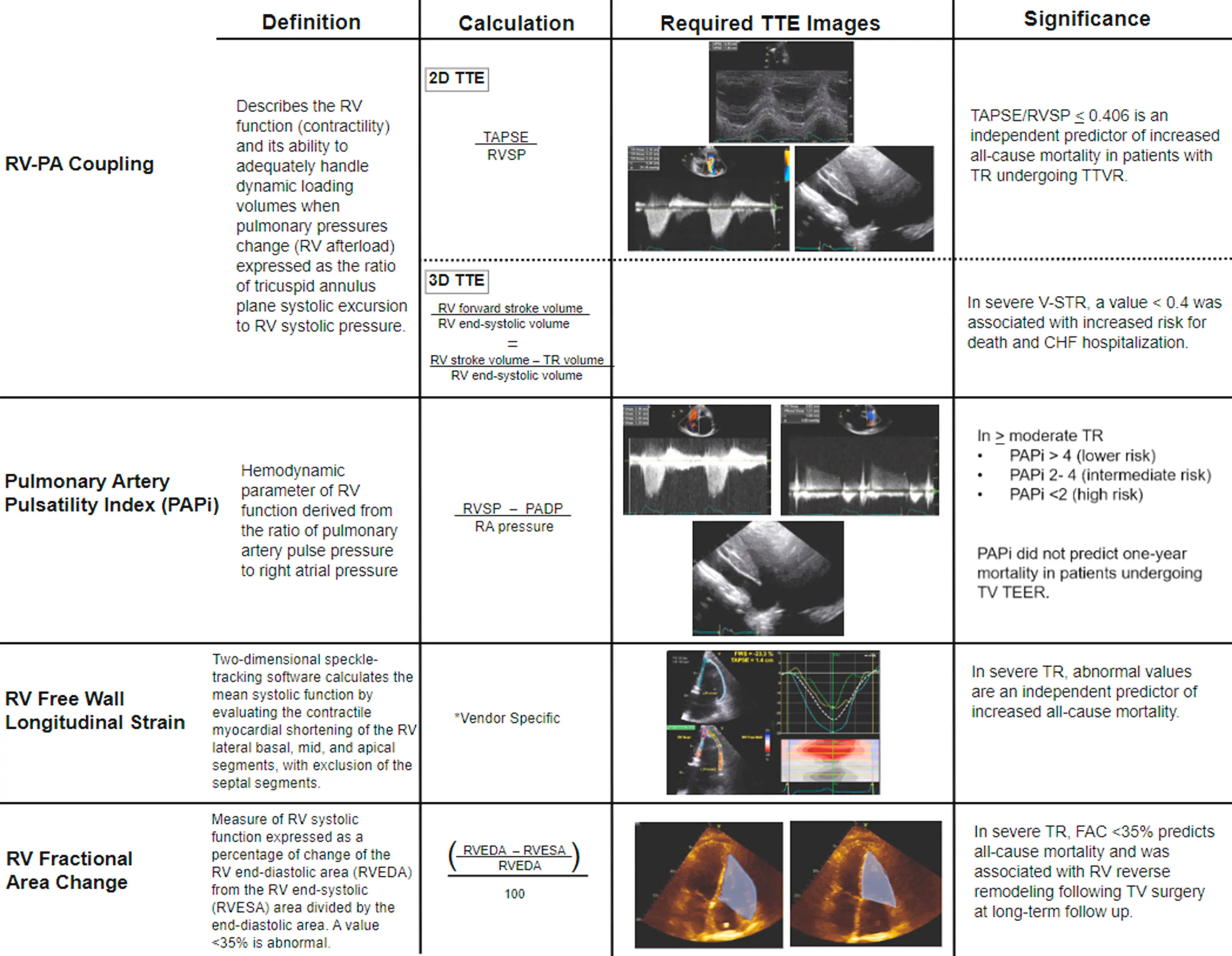 Figure source: 1
Figure source: 1
Cardiac MRI
- CMR is currently the reference standard for the quantitation of RV size and function.
Management
Severe, Symptomatic TR
 Figure source: 1
Figure source: 1
Valve Intervention
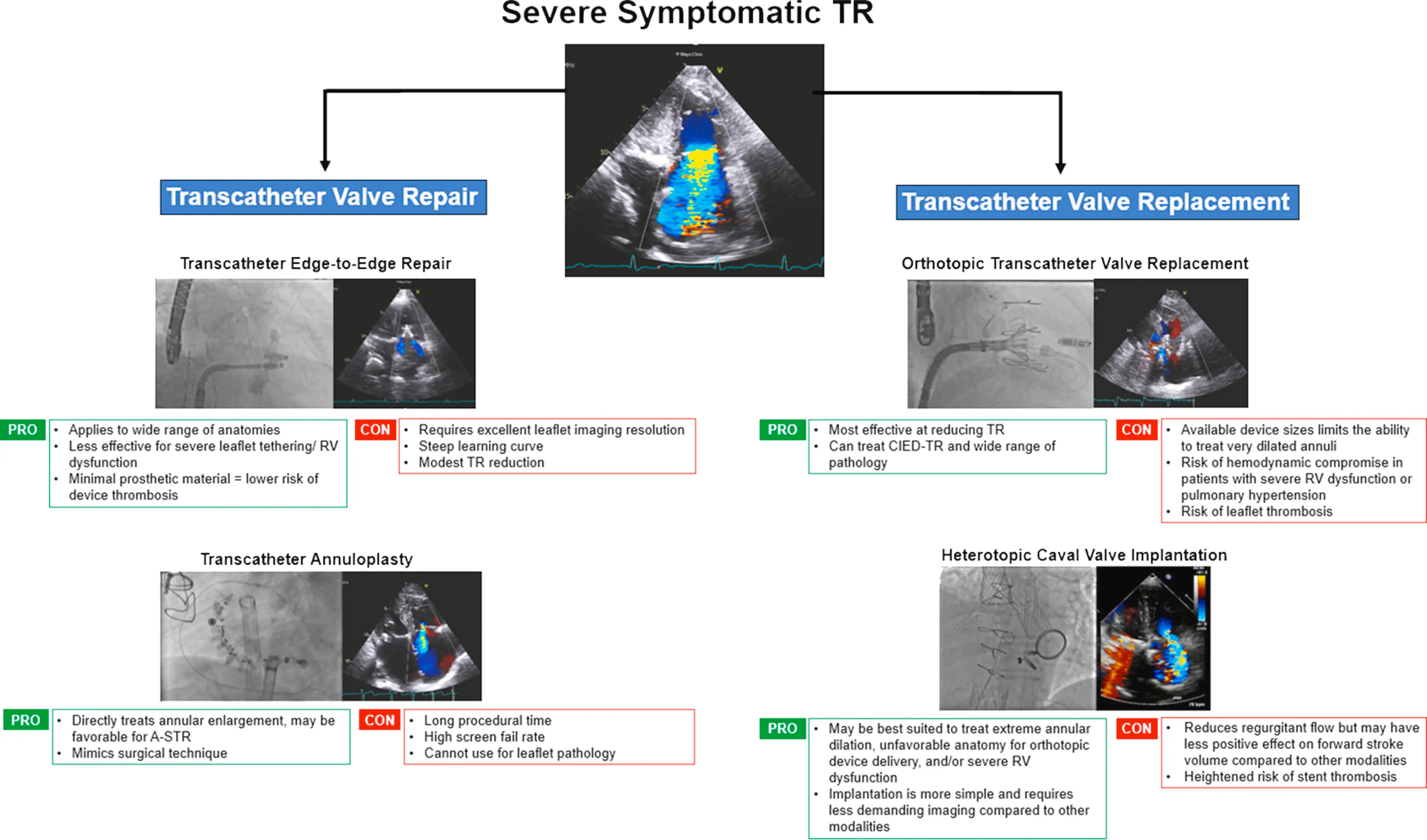 Figure source: 1
Figure source: 1
Footnotes
-
Welle GA, Hahn RT, Lindenfeld J, Lin G, Nkomo VT, Hausleiter J, Lurz PC, Pislaru SV, Davidson CJ, Eleid MF. New Approaches to Assessment and Management of Tricuspid Regurgitation Before Intervention. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2024 Apr 8;17(7):837-858. doi: 10.1016/j.jcin.2024.02.034. PMID: 38599687. ↩ ↩2 ↩3 ↩4 ↩5 ↩6 ↩7 ↩8
-
https://www.asecho.org/wp-content/uploads/2017/04/2017VavularRegurgitationGuideline.pdf ↩ ↩2 ↩3