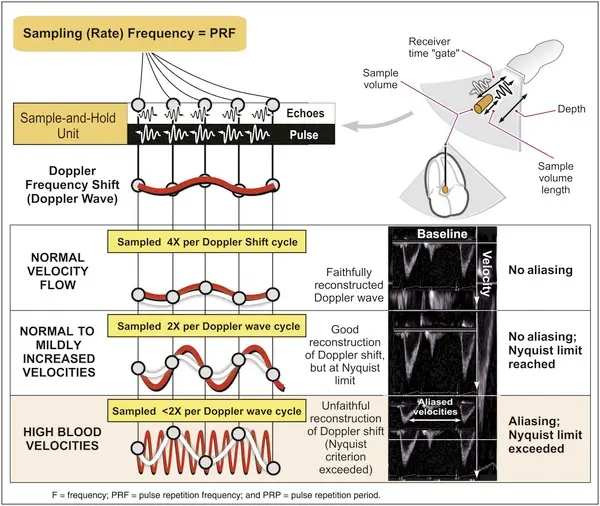
In PWD, a single ultrasound crystal sends to and receives sound beams from a single location by placing the “sample volume.” The crystal emits a short burst of ultrasound at a certain frequency (pulse repetition frequency). The ultrasound is reflected from moving RBCs and is received by the same crystal. Therefore, the maximal frequency shift that can be determined to one direction by PWD is one-half the PRF; this is called the Nyquist limit. (Oh, Chapter 4)
If the frequency shift is higher than the Nyquist limit, aliasing occurs. Aliasing refers to when the the Doppler spectrum/recording is cut off at the Nyquist limit, and the remaining frequency shift (translated into velocity) is recorded on the top or bottom of the opposite side. In other words, when the highest velocity a pulsed mode can measure is 130 cm/s in one direction, any velocity higher than the aliasing velocity is recorded from the top (when the actual flow moves away from the transducer) or from the bottom (when the actual flow moves toward the transducer) of the recording screen. (Oh, Chapter 4)
The PRF varies inversely with the depth of the sample volume: the shallower the location of the sample volume, the higher the PRF and the Nyquist limit (or Doppler velocity). (Oh, Chapter 4)
- Range specific (sample volume)
- Intermittent (pulsed) ultrasound at PRF and receives reflected wave
- PRF increases with shorter depth
- In other words, if you decrease your depth → ↑ PRF and ∴ ↑ Nyquist limit.
- pulsed ultrasound beam emits pulses at a pulse repetition frequency (PRF). If the Doppler frequency > PRF, a Doppler signal is produced that can’t be measured (aliasing). The maximum Doppler frequency that can be identified with pulsed Doppler is known as is the Nyquist limit and is usually around 2 M/s. Continuous Wave Doppler has no Nyquist limit.
- Common uses of PWD
- LVOT → LVOT VTI
- Mitral infows → E and A waves
- Pulmonary veins → assess MR, diastolic function, pulmonary stenosis
- RVOT → assess for Pulmonary Hypertension
- Hepatic veins → assess for flow reversal with severe TR, pericardial constriction, tamponade