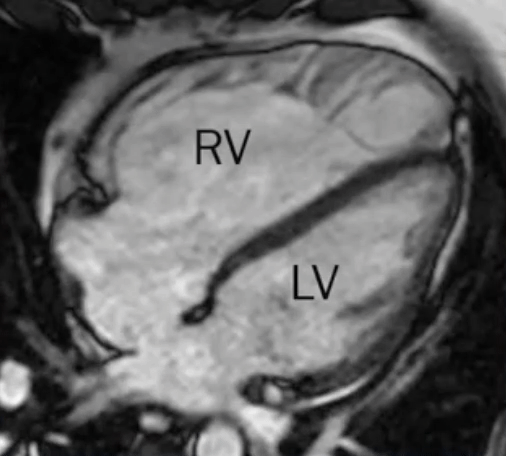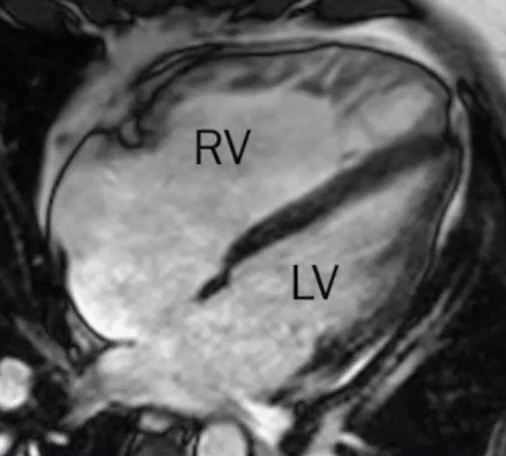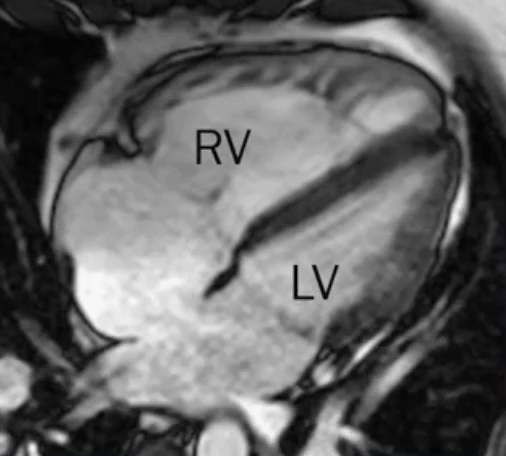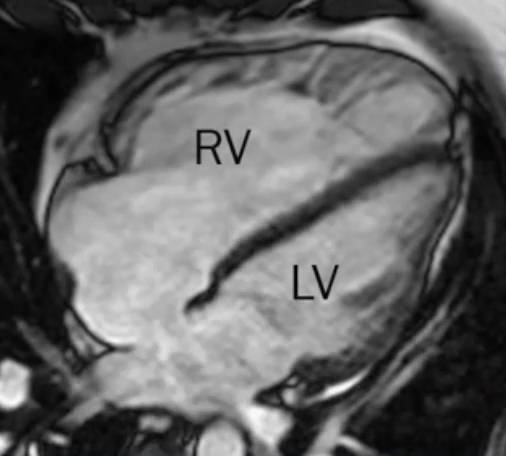
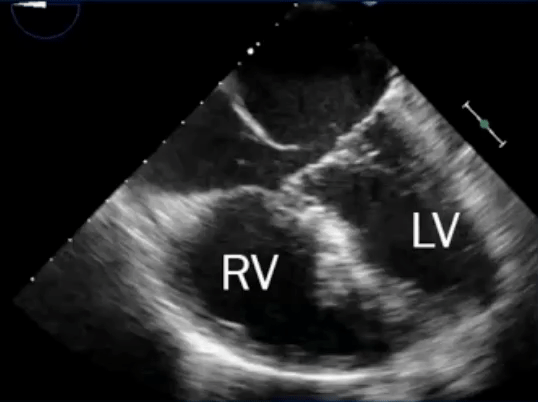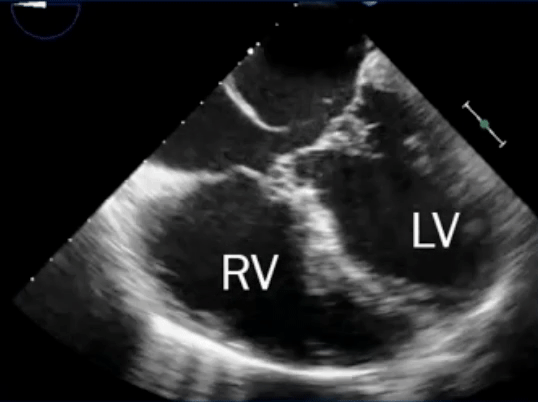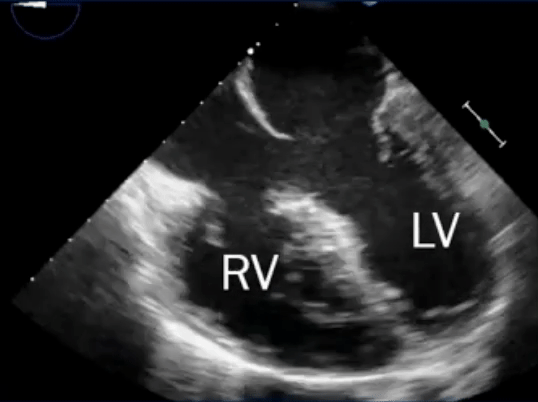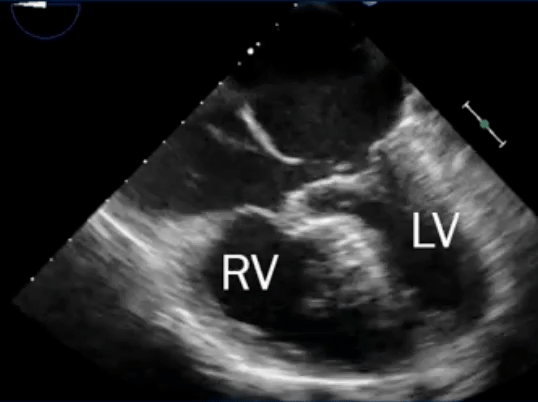
- L→R shunt causes overcirculation of the RA and RV → RA and RV enlargement
- Auscultation 👂
- Fixed-split S2
- Pulmonary flow murmur d/t ↑ blood flow across the pulmonary valve
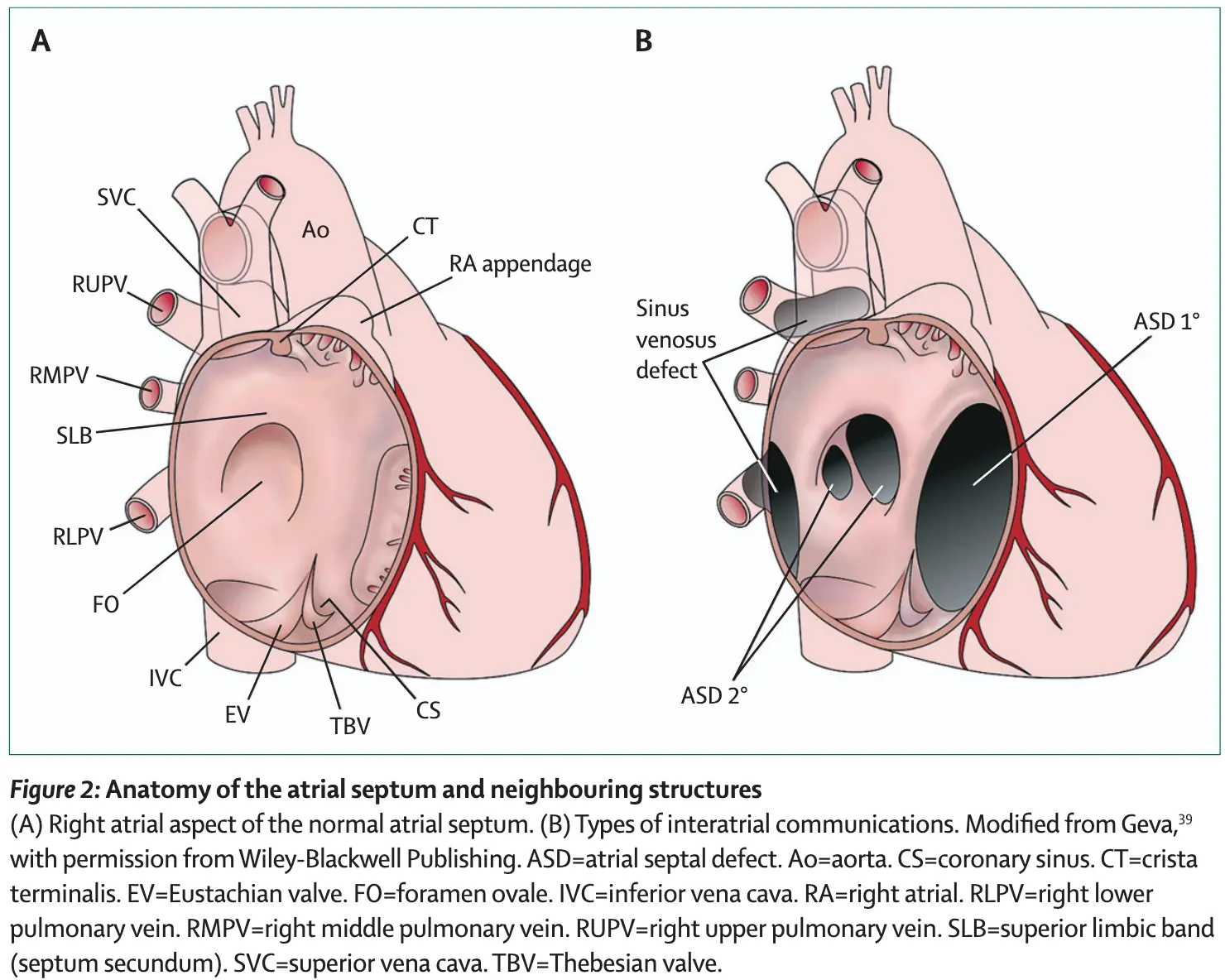 Figure source: 1
Figure source: 1
Secundum ASD
- Most common
- Often isolated
- ECG
- RBBB (complete/incomplete) and RAD
- TEE
- MRI
Primum ASD
- Part of AV septal defect with an interatrial communication located between the anterior-inferior margin of the fossa ovalis and the atrioventricular valves
- Associated with cleft MV, which causes MR
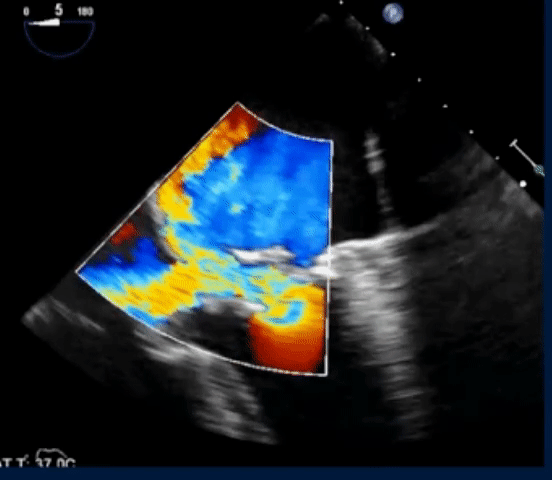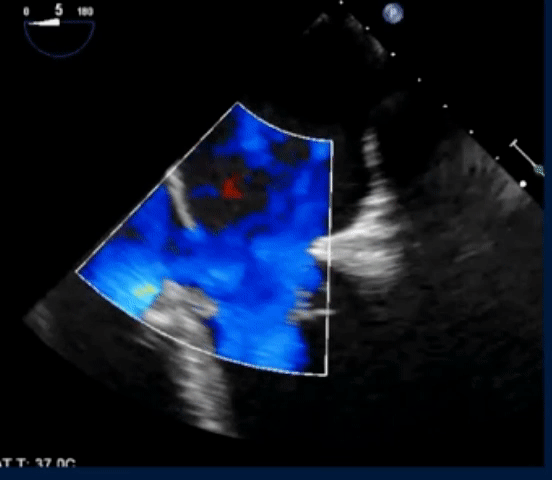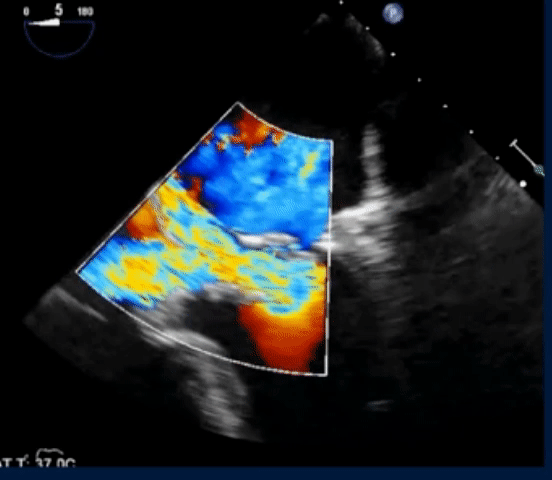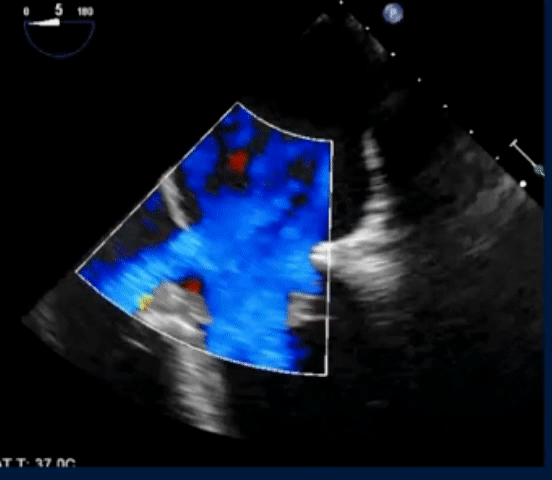
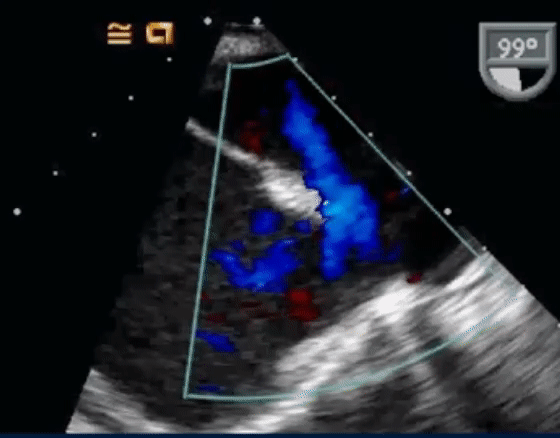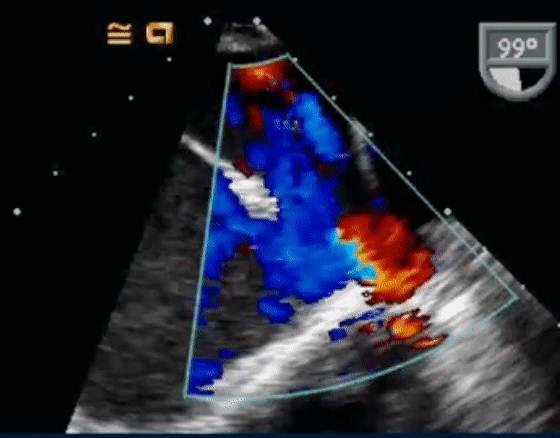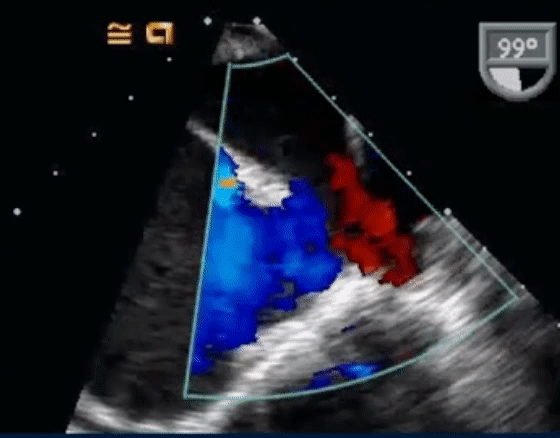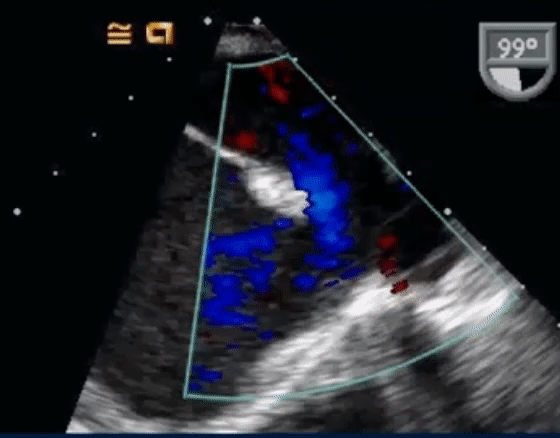
- The following TEE with color Doppler shows a jet of MR going into the LA and RA
- The following TEE with color Doppler shows a jet of MR going into the LA and RA
- ECG pattern is a board favorite 🌟
- RBBB (complete/incomplete) and LAD - d/t displacement of the AV node and a change in the configuration of the His-Purkinje fibers
- TEE
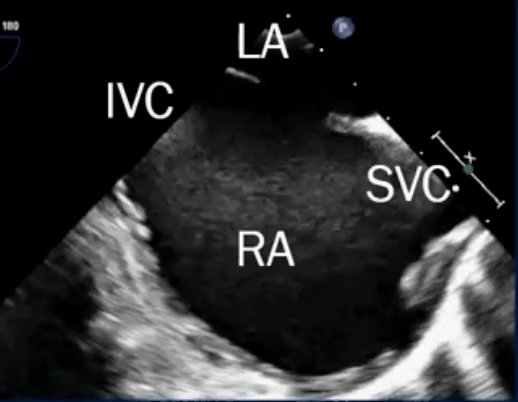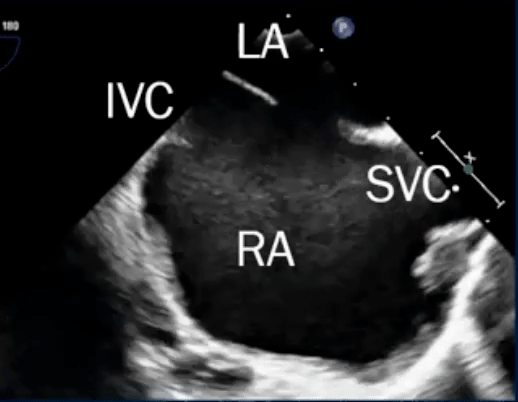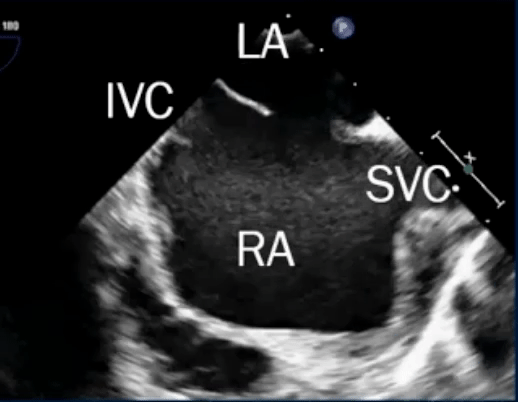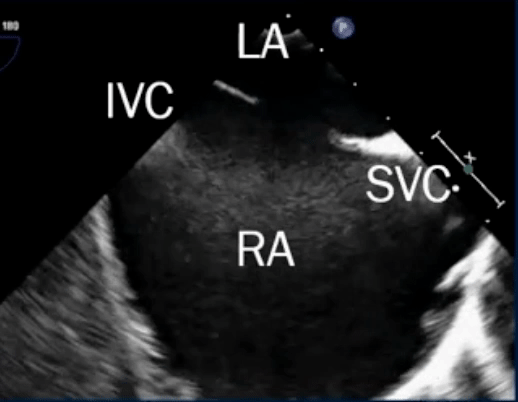
Sinus venosus defect
- Defects where the SVC/IVC reach the RA
- defect is a communication between one or more of the right pulmonary veins and the cardiac end of the superior vena cava (superior vena cava type) or the posterior-inferior atrial wall just above the inferior vena cava-right atrial junction (inferior sinus venosus defect) 1
- Most are SVC-type, i.e. superior sinus venosus defect in region of SVC-RA junction
- Associated with PAPVR (RUPV > RMPV/RLPV)
- Can be difficult to see on TTE, ∴ TEE, CMR, or CT needed.
- Post-repair, it is not uncommon to have Sinus Node Dysfunction (SND)
- TEE below shows bicaval view. To identify the superior sinus venosus defect (i.e. SVC type), you’ll want to pay attention to the SVC area as highlighted in this image.
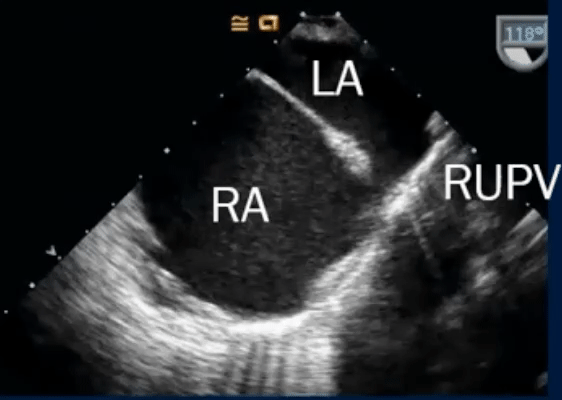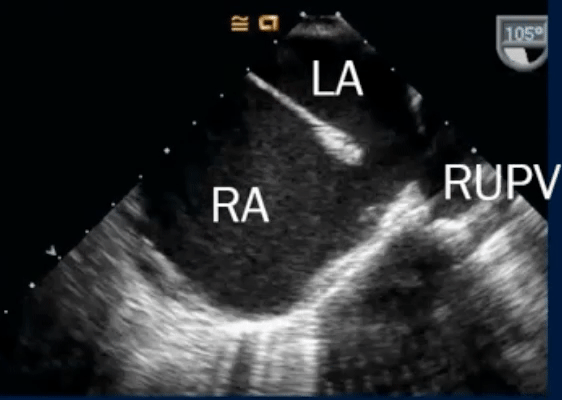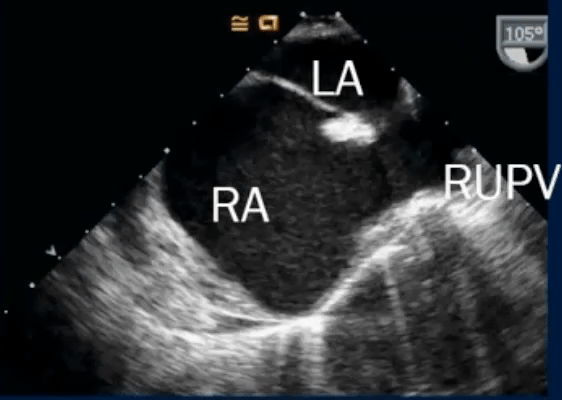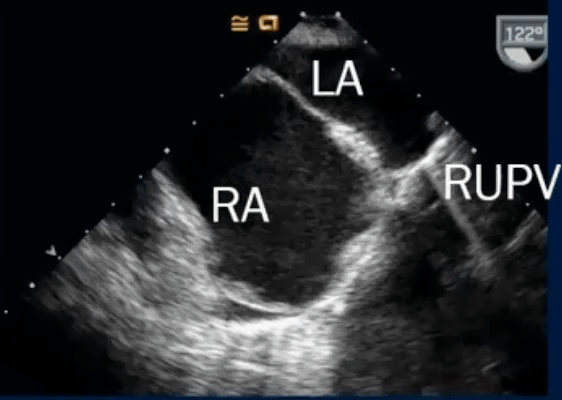
- On Color Doppler, we see the blue flow going from LA to the RA through the superior sinus venosus defect:
Echo
- “Late” inter-atrial shunt if bubbles cross > 5 beats(?)
- Look up ASE guidelines on ASD. There was mention of 3-6 beats indicating possible intrapulmonary shunt