- Related:
The analogy that is often used to describe stenotic lesions is covering a hose with your finger, you can sense the increased pressure when doing so. Further, this causes the jet of water to travel a greater distance.
- Auscultation
- Opening snap (OS)
- forceful opening of the MV when the pressure in the LA is greater than the pressure in the LV → OS of MS is a high-pitched early diastolic sound due to sudden tensing of the valve leaflets and subvalvular apparatus at the end of the opening excursion (Source)
- occurs 40-120 milliseconds after A2
- A2-OS interval varies inversely with the severity of mitral stenosis
- Opening snap (OS)
- In a patient with rheumatic MS who has Sx, but there is a discrepancy with resting echo hemodynamics, then do exercise testing with hemodynamics
- exercise is preferred to dobutamine stress because it provides a more physiologic assessment
- Screening surveillance
- Asymptomatic patients with mild or moderate MS should have surveillance echocardiograms every 3-5 years
- Severe, but asymptomatic:
- if MVA <1 cm2 → exercise treadmill testing should be performed yearly
- if MVA 1-1.5 cm2: every 1-2 years
| Mild | Moderate | Severe | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Valve area (cm2) | >1.5 | 1.0-1.5 | <1.0 |
| Mean gradient (mmHg) | <5 | 5-10 | >10 |
| PA pressure (mmHg) | <30 | 30-50 | >50 |
| Diastolic PHT (ms) | <150 | ≥150 | |
| The above criteria are based on a HR between 60 to 80 bpm and in sinus rhythm. |
📝 Because of the variability of the mean pressure gradient with HR and forward flow, you may not see it included in the criteria for severity.
| Stage | Definition | Valve Anatomy | Valve Hemodynamics | Hemodynamic Consequences | Symptoms |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | At risk of MS | Mild valve doming during diastole | Normal transmitral flow velocity | None | None |
| B | Progressive MS | Rheumatic valve changes with commissural fusion and diastolic doming of the mitral valve leaflets Planimetered mitral valve area >1.5 cm2 | Increased transmitral flow velocities Mitral valve area >1.5 cm2 Diastolic pressure half-time <150 ms | Mild to moderate LA enlargement Normal pulmonary pressure at rest | None |
| C | Asymptomatic severe MS | Rheumatic valve changes with commissural fusion and diastolic doming of the mitral valve leaflets Planimetered mitral valve area ≤1.5 cm2 | Mitral valve area ≤1.5 cm2 Diastolic pressure half-time ≥150 ms | Severe LA enlargement Elevated PASP >50 mm Hg | None |
| D | Symptomatic severe MS | Rheumatic valve changes with commissural fusion and diastolic doming of the mitral valve leaflets Planimetered mitral valve area ≤1.5 cm2 | Mitral valve area ≤1.5 cm2 Diastolic pressure half-time ≥150 ms | Severe LA enlargement Elevated PASP >50 mm Hg | Decreased exercise tolerance Exertional dyspnea |
| Source: Table 16 of Otto et al. |
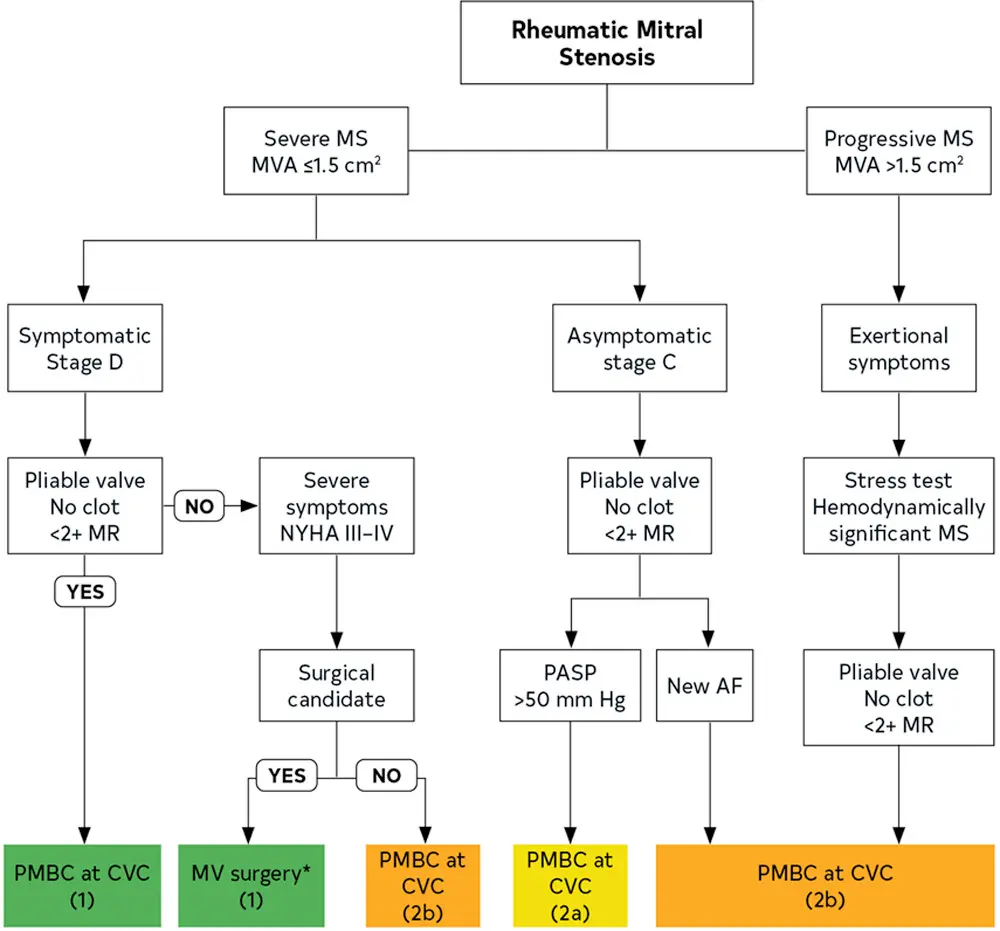
Severe MS
- Mitral valve area (MVA) is considered significantly narrowed when <1.5 cm2
Wilkins Score for Balloon Valvuloplasty
- Wilkins Echo score can predict the procedural success for mitral valvuloplasty based on valve structure.
- Grades each of the following components from 1 to 4:
- leaflet mobility
- leaflet thickness
- calcification
- abnormalities of the subvalvular apparatus
- Wilkins score ≤ 8 predicts a more favorable procedural, short, intermediate and long-term outcome (including survival).
Echo in MS
- MS severity is assessed in 3 ways:
- Doppler pressure gradient
- Mean gradient is more important than peak gradient
- ⚠️ may overestimate severity when transmitral flow is ↑ (e.g., with concomitant MR) and may also be misleading when ventricular compliance is abnormal
- Direct planimetry of MVA
- Preferred approach as it is it is independent of loading conditions
- Pressure Half Time (PHT) method
- The more severe the MS, the slower the emptying into the LV and the longer the PHT will be.
- ⚠️ may be inaccurate in patients with abnormalities of LA or LV compliance, those with associated aortic regurgitation, and those who have had recent mitral valvuloplasty.
- ⚠️ has not been validated in patients with calcific MS
- Doppler pressure gradient
Echo Math for MS
MVA using PHT
MVA using PISA method
Management