- Phased matrix array with 3000 elements
- Capable of acquiring pyramidal volumes with varying temporal resolution
- Multiple 3D modes of acquisition
- Live 3D
- 3D Zoom
- Full Volume
- 3D Color Flow
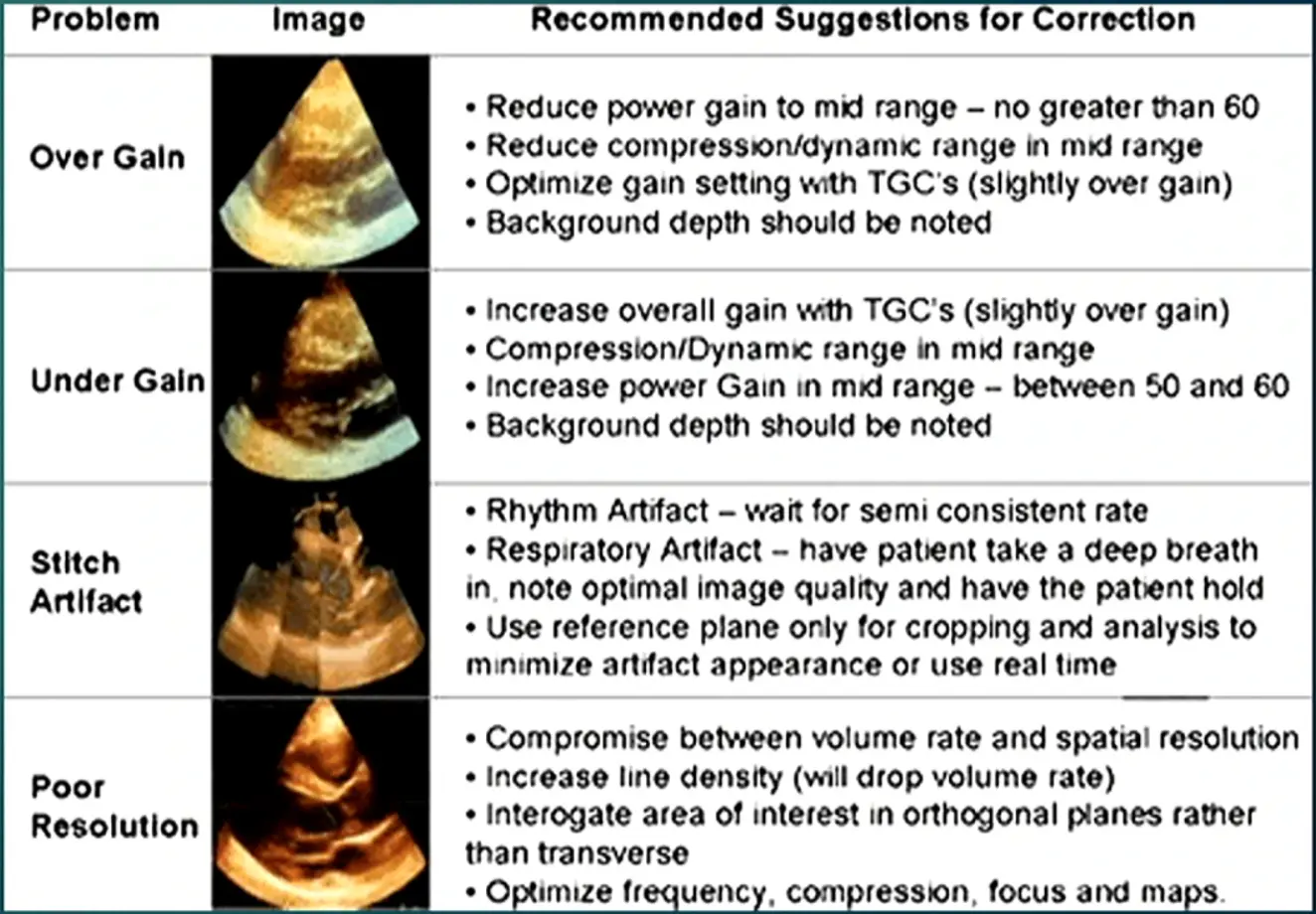
3D Echo Physics
- Recall, ultrasound speed in tissue: 1500 m/s
- Pulse repetition period for a depth of 16 cm: 220 us
- Time to acquire one frame = PRP * scanlines
- 2D echo (90 scanlines): 90 ms to acquire one frame (50 Hz)
- 3D echo (2400 scanlines): 528 ms to acquire one frame (1.9 Hz) → can appear very “choppy”, so use Echo tricks to improve temporal resolution
- limit acquisition to area of interest
- To improve temporal resolution
- Decrease depth
- Decrease lateral width
- Cardiac cycle gating
- To improve spatial resolution (crispness/sharpness)
- Increase scan line density
- However, there is a tradeoff as this decreases temporal resolution
- Increase scan line density
3D Acquisition Modes
- Live 3D (Narrow View)
- Gross assessment of valve function
- 3D Zoom
- Real time valvular assessment (intra-op)
- Structural interventional procedures
- Full Volume
- Assess LV function
- Evaluate valve function
- Assess valvular stenosis
- Structural interventional procedure, intra-op procedures
- TAVR evaluation
- 3D Color Flow
- Assessment of valvular regurgitation
- Assessment of perivalvular leak
- Artifacts
Live 3D (Narrow angle)
- Live 3D is a setting that provides for real time 3D imaging without the need for cardiac gating while maintaining good spatial and temporal resolution.
- Disadvantage: Small volume (60 x 30 degrees) compared to full volume (100 × 100 degrees)
- Good for gross visualization of cardiac structures and interventional procedures. Not as useful for quantitative analysis.
3D Zoom
- Used often looking at the Mitral Valve
- Similar to Live 3D but smaller angles (30 x 30 degrees)
- Good temporal and spatial resolution, can customize zoom for valves.
- Useful for structural interventional procedures
- Disadvantages include small pyramidal volume and loss of spatial resolution if the operator “zooms” in too much.
Full Volume
- Not commonly used, but powerful tool in your toolbox
- 100 x 100 degree view
- Can have good temporal and spatial resolution
- Disadvantages
- Operator intensive for image optimization
- Needs gated images for good temporal resolution
- Requires significant cropping
3D Color Flow
- 40 × 40 degree view
- Superimposes color Doppler flow over tissue images
- Useful for valve regurgitation quantification
- Can get a 3D vena contracta
- Disadvantages
- Needs gating for good temporal resolution
- Small pyramidal volume
Knobology
- Minimize depth and width to bracket area of interest
- Adjust gain and TGC for good 2D image
- If doing 3D color flow, turn on color Doppler to include area of interest
- Adjust elevation and lateral width/position
- Choose 3D chroma map H, color scale 2
- Better use of blue/bronze shading to convey depth
- If NSR, gate over 2-4 beats
- If AFib, choose HVR (interlaced, good temporal, poor spatial)
- Can also do 1-beat gating (poor temporal resolution, better spatial)
- HVR is roughly equal to 4 beat gating re: temporal resolution (mediocre for afib 3D color flow)
- Dr. Saghir showed an example where he switched to HVR and could see paravalvular leak much better.
- View MPR cuts for stitching, hit acquire if satisfied
Cropping
- Can crop a live full volume for “real time” imaging Make sure you include landmarks in the crop Fixed plane method • Selectable rectangles representing different axes Steerable plane • “Shave” volume with a steerable plane
- 🌟I-Crop
- Create a crop based on boxes on orthogonal 2D views After crop is made and positioned, decrease gain and compression to bring out area of interest Adjust smoothening if necessary Hit acquire
LVEF
Proper assessment has implications for mortality / morbidity Important for assessment of response to treatment Implications regarding ICD implantation Important for surgical planning in severe valvular regurgitation Cardio-oncology
Methods for LVEF assessment
M-Mode assessment (Quinone’s method) • Regional wall motion abnormalities (apical) decrease accuracy Modified Simpson’s Method (Volume of discs) • Requires good endocardial border visualization • Subject to errors in measurement due to foreshortening Subjective assessment 3D assessment
Valvular Stenosis
- 2D planimetry often misses true valve orifice
- 3D planimetry allows adjustment of plane to view true valve orifice
- Full volume acquisition, can do with 3D Zoom
- Minimize depth and lateral width to encompass only the valve
- Gate over 2-4 cardiac cycles for best temporal resolution
- QLAB
- 3D continuity equation — never really took off even though 2D approach is prone to error
- AVA = 3D SV / CW AV VTI
- MVA = 3D SV / CW MV VTI
Valvular Regurgitation
- 3D color flow allows the visualization of the vena contracta with careful cropping
- May be superior to PISA and 2D vena contracta as 3D VC avoids geometric assumptions
- 3D color Doppler is useful in “hard to find” mitral regurgitation
- Dr. Saghir had nice example showing Aortic Regurgitation using 3D VC to support severe AI.
Saghir’s take on 3D Echo
This is an adjuvant, not a replacement to 2D echo Focused 3D echo • If LVEF is low, consider 3D LVEF (TTE) • If MR is at least moderate, consider 3D MV view and 3D VC • If MS, consider 3D planimetry • If AR is at least moderate, consider 3D VC • If AS, consider 3D planimetry • 3D continuity equations for AS and MS With practice, the above methods require little additional time to a trained operator and could decrease chance of delayed diagnosis of significant pathology.
Advanced 3D applications
Congenital cardiology • 3D RV volume and systolic function • 3D evaluation of aortopathies (Marfan’s, thoracic aneurysm) Electrophysiology 3D LA size for afib ablation 3D LA strain re: maintenance of NSR following cardioversion or ablation General cardiology • 3D images with dobutamine stress testing