- Multisystem granulomatous disease
- Unknown etiology
- Results in arrhythmias, HF and SCD
- Second leading cause of sarcoidosis-related mortality
- #1 is pulmonary
- Increasing prevalence? Or are we just doing better with diagnosis?
- Diagnostic uncertainty is common
- Yield of EMB isn’t high b/c disease often patchy
- Risk stratification is challenging
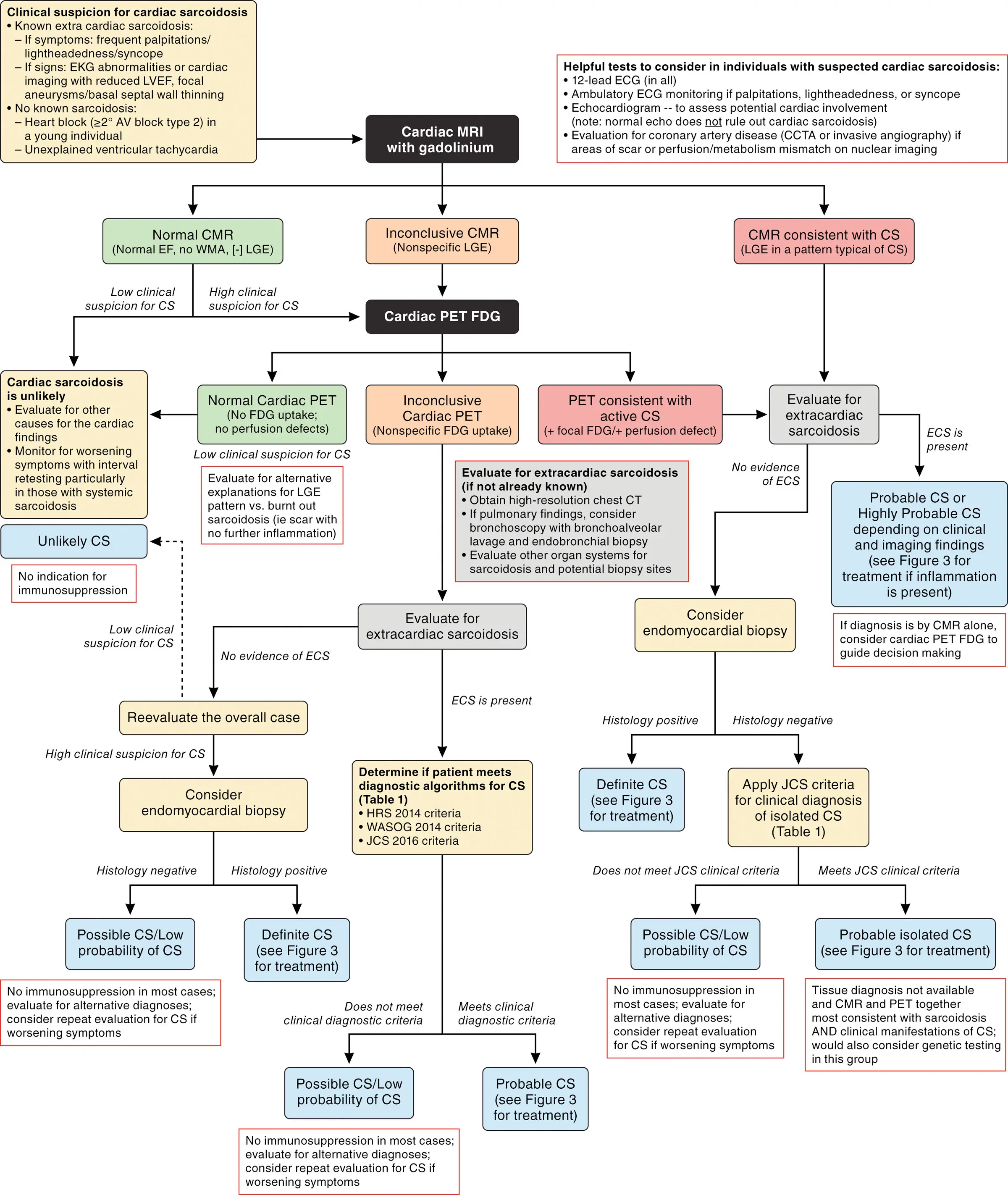
Diagnosis
- Diagnostic criteria
- HRS criteria
- TODO
- JCS criteria
- TODO
- WASOG criteria
- HRS criteria
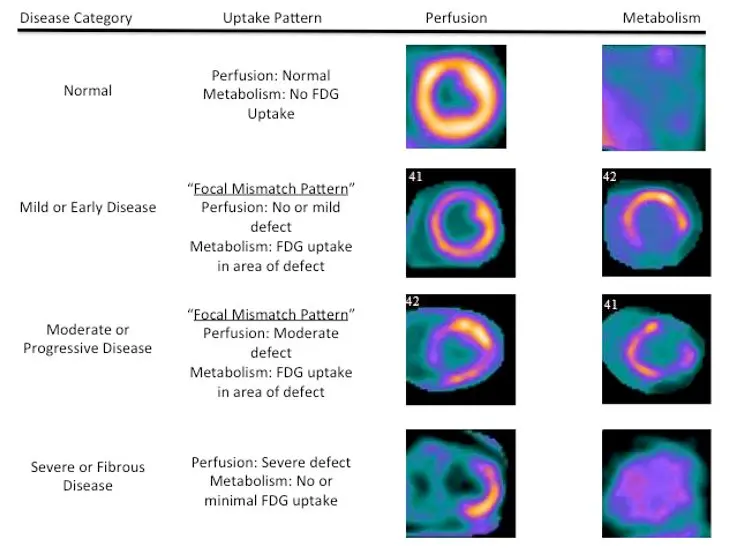
FDG-PET
- Assess disease activity and monitor therapy response
- Whole body PET can identify extracardiac biopsy sites
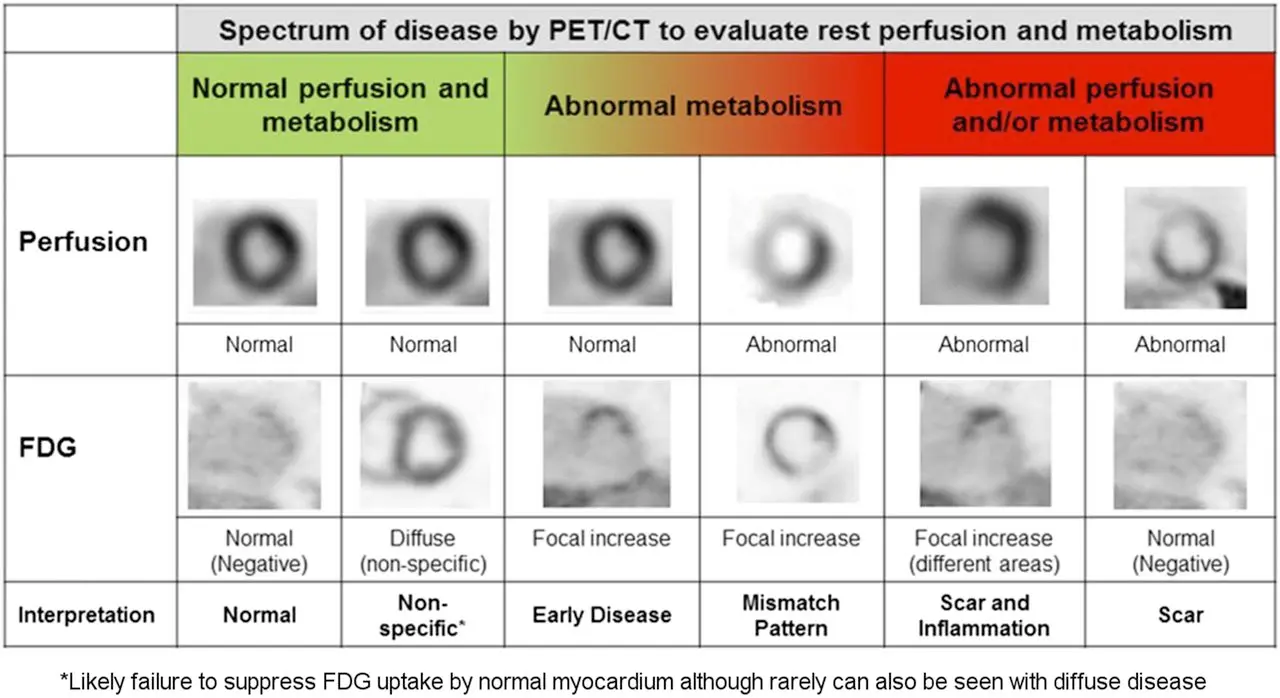
- Mismatch in perfusion and metabolism is highly specific (100%, 83% sensitive)
- Any FDG uptake pattern specificity can be as low as 33%
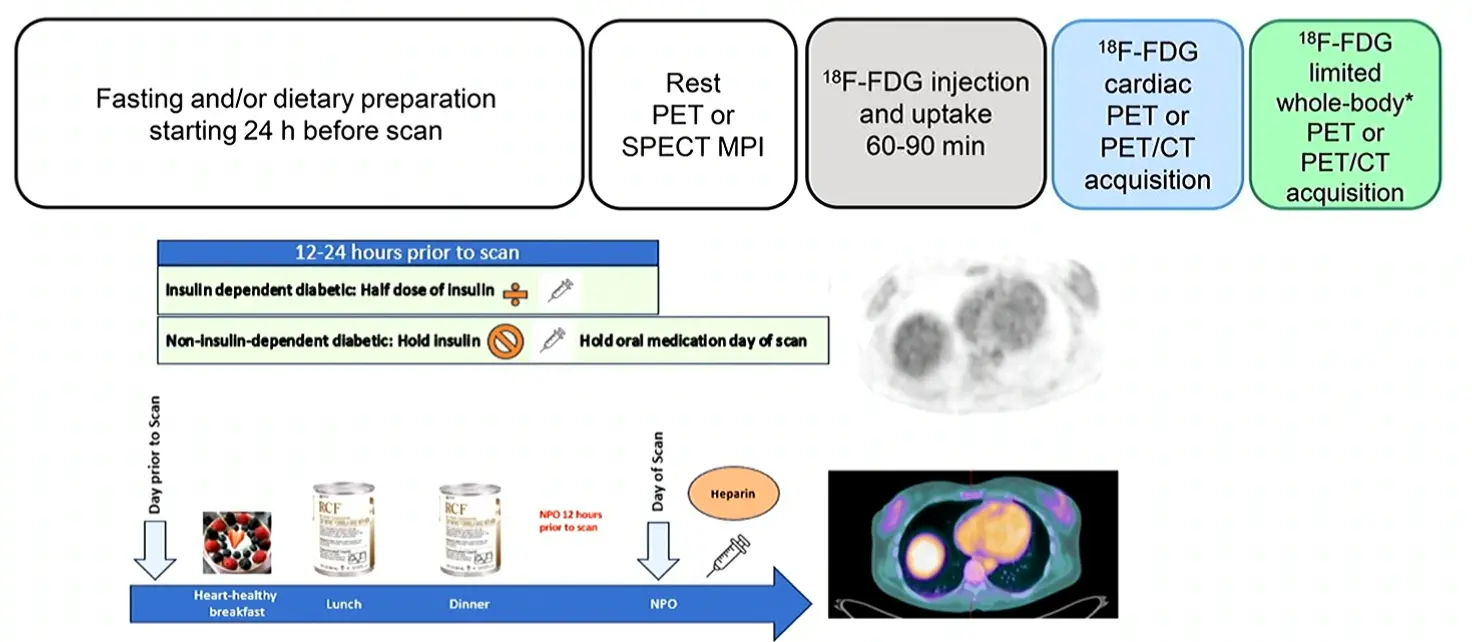
- Patient preparation is key 🔑
- It has to be endogenous ketosis, i.e. by fasting (KEE-TOSIS study)
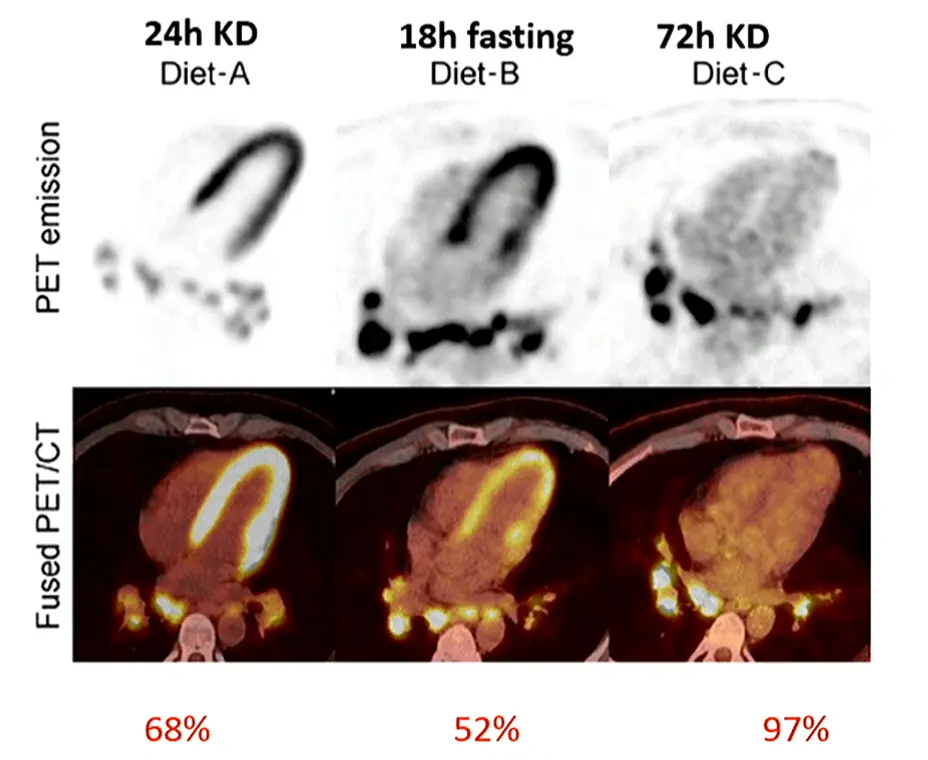
- Highlights that sometimes longer fasting yields better results (even if you have to go to 72 hours!)
- Must rule out ischemic heart disease
- b/c ischemic cells with take up FDG, which can be misleading. Ischemia induces translocation of GLUT4 to cell membrane
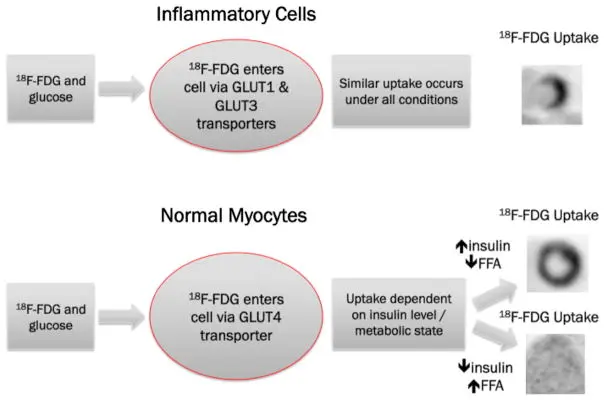 Figure source
Figure source
Whole Body PET
- Limited whole-body PET study using the same 18F-FDG injection should be performed in addition to the dedicated cardiac 18F-FDG study
- Should include the chest, liver, and spleen
- Can be interpreted even if poor dietary preparation or non-cardiac protocol
- SUV of index nodes should be measured
- CT for AC can assess presence of LAD
- Mismatch pattern is highly specific for sarcoidosis
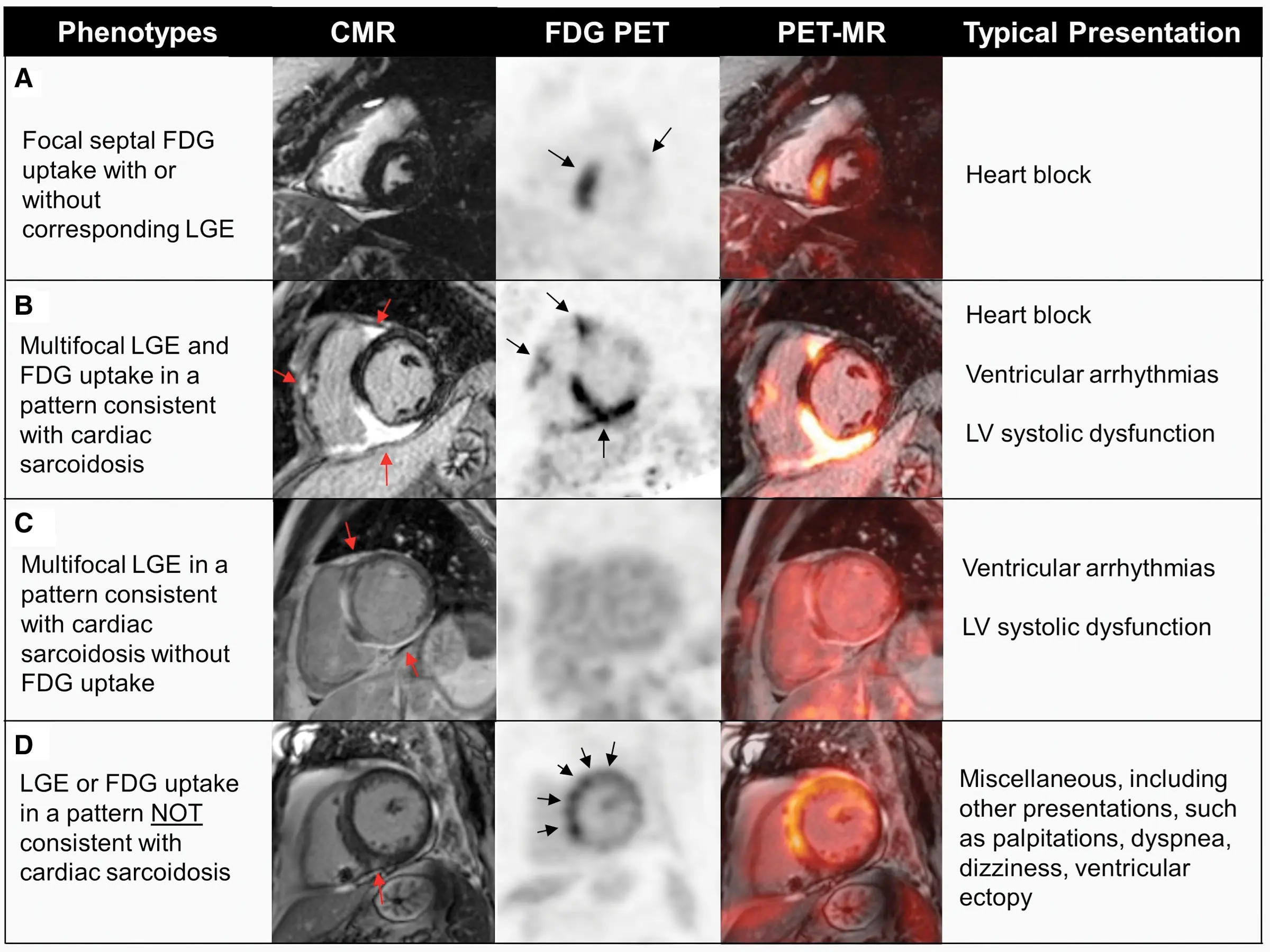
MRI
CMR has a high NPV, so obtain CMR only in low clinical suspicion. Obtain CMR and PET when high clinical suspicion
- No preparation is needed
- May identify other causes of cardiomyopathy
- Ideally obtained at baseline, prior to PPM/ICD
- If PPM is present, artifact tends to be minimal
- If ICD is present, artifact tends to be significant, and results are less accurate. Use wide band imaging and lift device as high as possible.
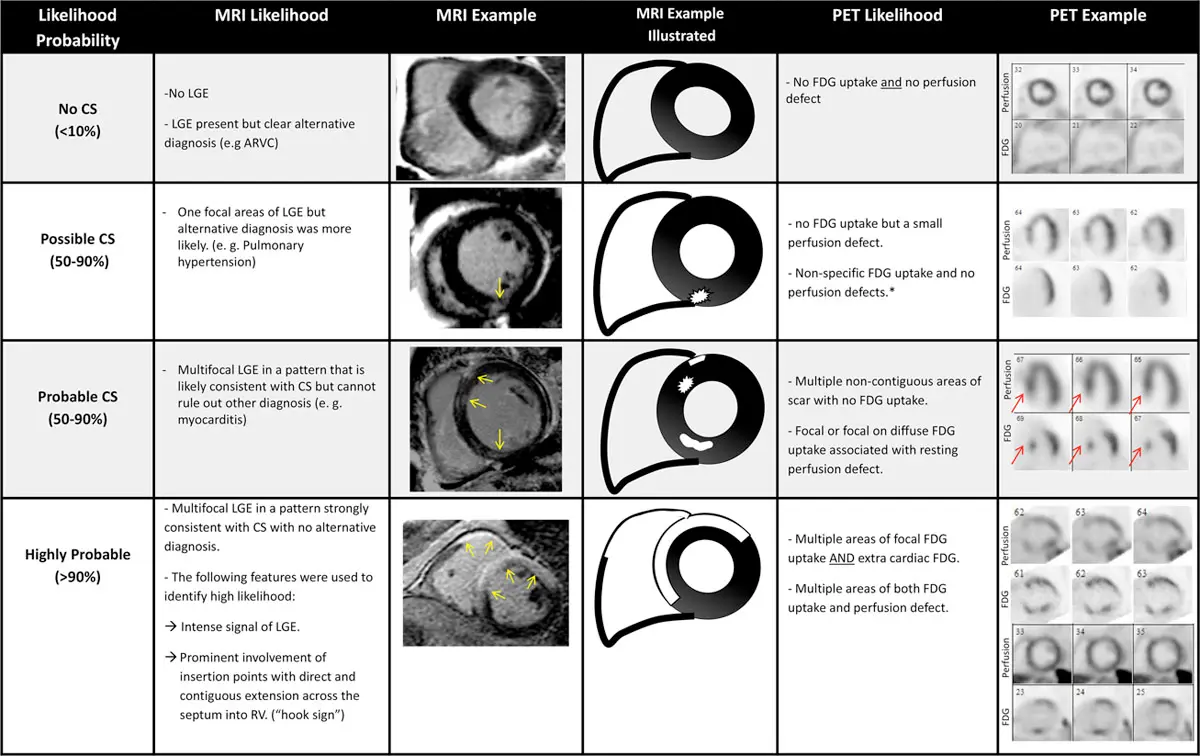
Interpretation with MRI:
- T1/2 mapping, T2-weighted edema imaging and LGE are most important sequences
- LGE carries the strongest prognostic value
- 95% sensitivity, 85% specificity
- Typical pattern: multifocal multi-pattern LGE with septal and RV involvement. More specific but no pattern is 100% specific.