Approach to Hyperlipidemia
- Rule out secondary causes
- Assess risk: Ask 3 Questions
- Discuss lifestyle & options
- Initiate treatment & monitor
flowchart TD A[Is ASCVD present?] --> |Yes| B("Secondary Prevention\nGoal LDL < 55 (very high risk) or < 70") A --> |No| C(Primary Prevention) C --> D[Is LDL ≥ 190 mg/dL?] D --> |Yes| E([Familial Hyperlipidemia\nGoal LDL < 55/70]) D --> |No| F[Is DM Present?] F --> |Yes| G([T1DM or T2DM\nGoal LDL < 55/70/100]) F --> |No| H([No DM\nGoal LDL < 55/70/100])
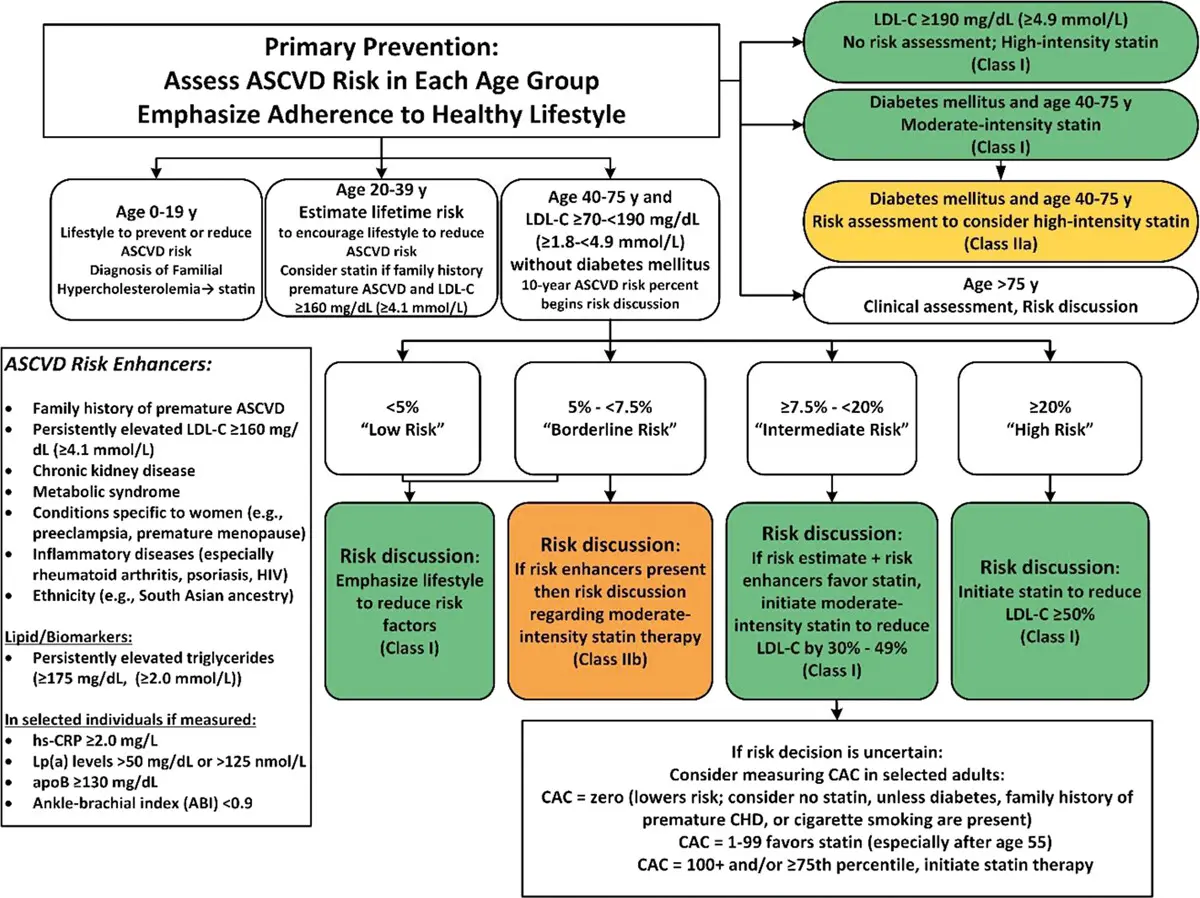
flowchart TD A[Primary Prevention\n no DM] --> B["AHA/ACC ASCVD Risk\nEstimator Plus\n(40-75 yo)"] B --> |"High (≥ 20%)"| C([High-intensity Statin]) B --> |"Intermediate (7.5-<20%)"| E(["Evaluate 'Risk-Enhancers'\nIf +: moderate statin"]) E --> H["If uncertain, check CAC"] B --> |"Borderline (5-<7.5%)"| F(["Evaluate 'Risk-Enhancers'\nIf +: moderate statin (IIb)"]) B --> |"Low (≤5%)"| G([Lifestyle Mod])
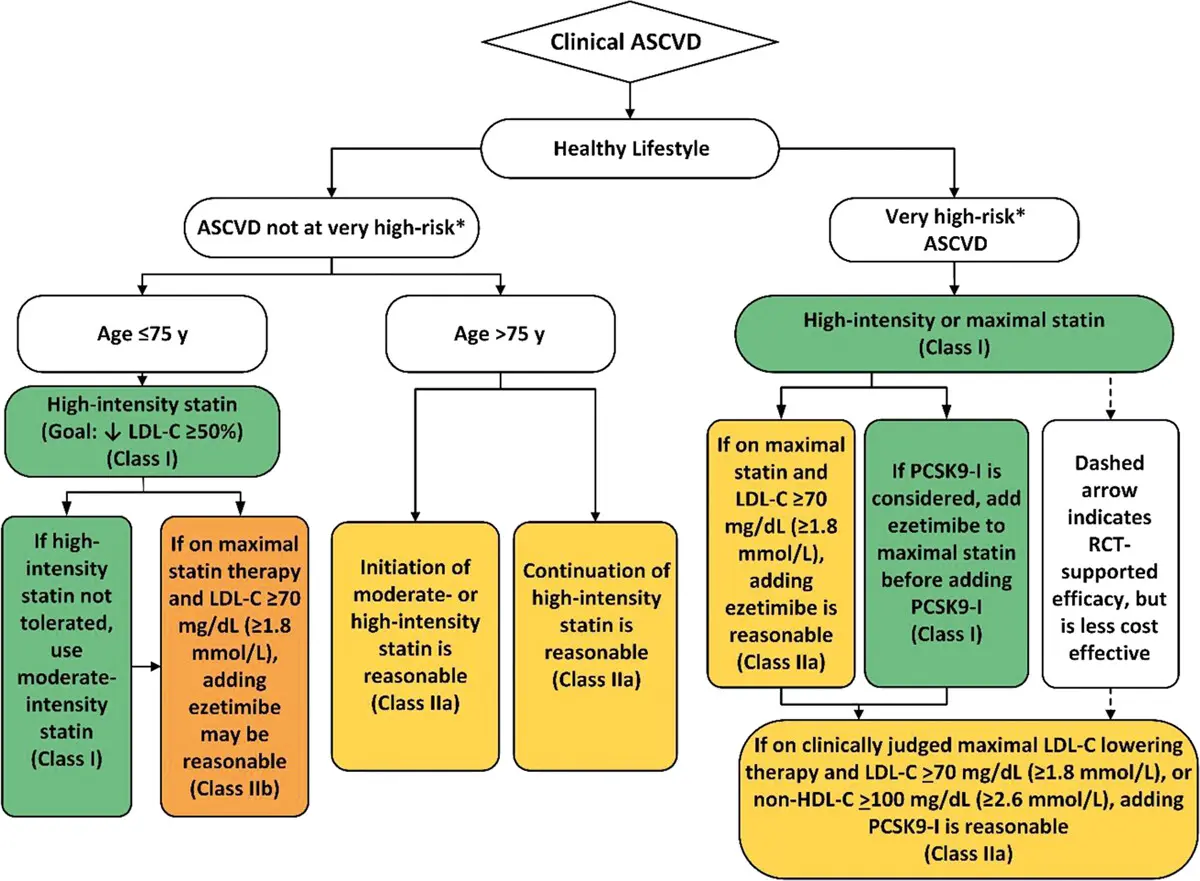
Very High Risk ASCVD
- Very High Risk ASCVD is if patient has had ≥ 2 ASCVD events or (1 Event + ≥ 2 Conditions)
- Events
- Conditions
- Current smoker, DM, HTN, ≥65 years
- LDL ≥ 100 on max statin & ezetimibe therapy
- Heterozygous FH
- Prior CABG/PCI (Not major ASCVD event)
- CKD (eGFR 15-59)
- Hx of Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection Fraction (HFrEF)

- Figure source: 1
‘Risk Enhancers’
- Diabetes “Risk Enhancers” → if present, LDL goal < 70; if not present, then LDL goal < 100
- Duration:
- T2DM for 10 years
- T1DM for 20 years
- Ur Albumin ≥30 mcg/mg Creat
- eGFR <60 ml/min/1.73 m2
- Diabetic retinopathy
- Diabetic neuropathy
- ABI <0.9
- Duration:
- Primary Prevention ‘Risk Enhancers’
- History and Co-morbidities (Think Inflammation)
- Fam Hx premature ASCVD
- Ethnicity (eg, South Asian ancestry)
- CKD
- Metabolic Syndrome
- Conditions specific to women (eg, Pre-eclampsia, premature menopause)
- Inflammatory diseases (esp Rh Arthritis, psoriasis, HIV)
- Lipids/Biomarkers
- LDL-C ≥ 160
- Persistently elevated TG ≥175
- Other
- hsCRP ≥ 2.0
- ABI < 0.9
- Lp(a) >50 mg/dL or 125 nmol/L
- especially if Fam Hx of premature ASCVD Risk Calculator
- ApoB > 130 mg/dL
- especially if TG > 200
- History and Co-morbidities (Think Inflammation)
Secondary Causes of HLD Commonly Encountered
| Secondary Cause | Elevated LDL-C | Elevated TG |
|---|---|---|
| Diet | Saturated fat or keto, weight gain, anorexia | Weight gain, very low-fat diet, high refined carbs, excess alcohol |
| Drugs | Diuretics, Amiodarone, retinoic acid (even topical), glucocorticoids, cyclosporine | Beta-blockers (except carvedilol), thiazides, anabolic steroids, retinoic acid, oral estrogens, glucocorticoids, protease inhibitors, sirolimus, raloxifene, tamoxifen |
| Diseases | Biliary obstruction, Nephrotic syndrome | Nephrotic syndrome, chronic renal failure, lipodystrophies |
| Disorders of metabolism | Low T4, obesity, pregnancy | DM (poorly controlled), Low T4, obesity, pregnancy |
LDL Goals
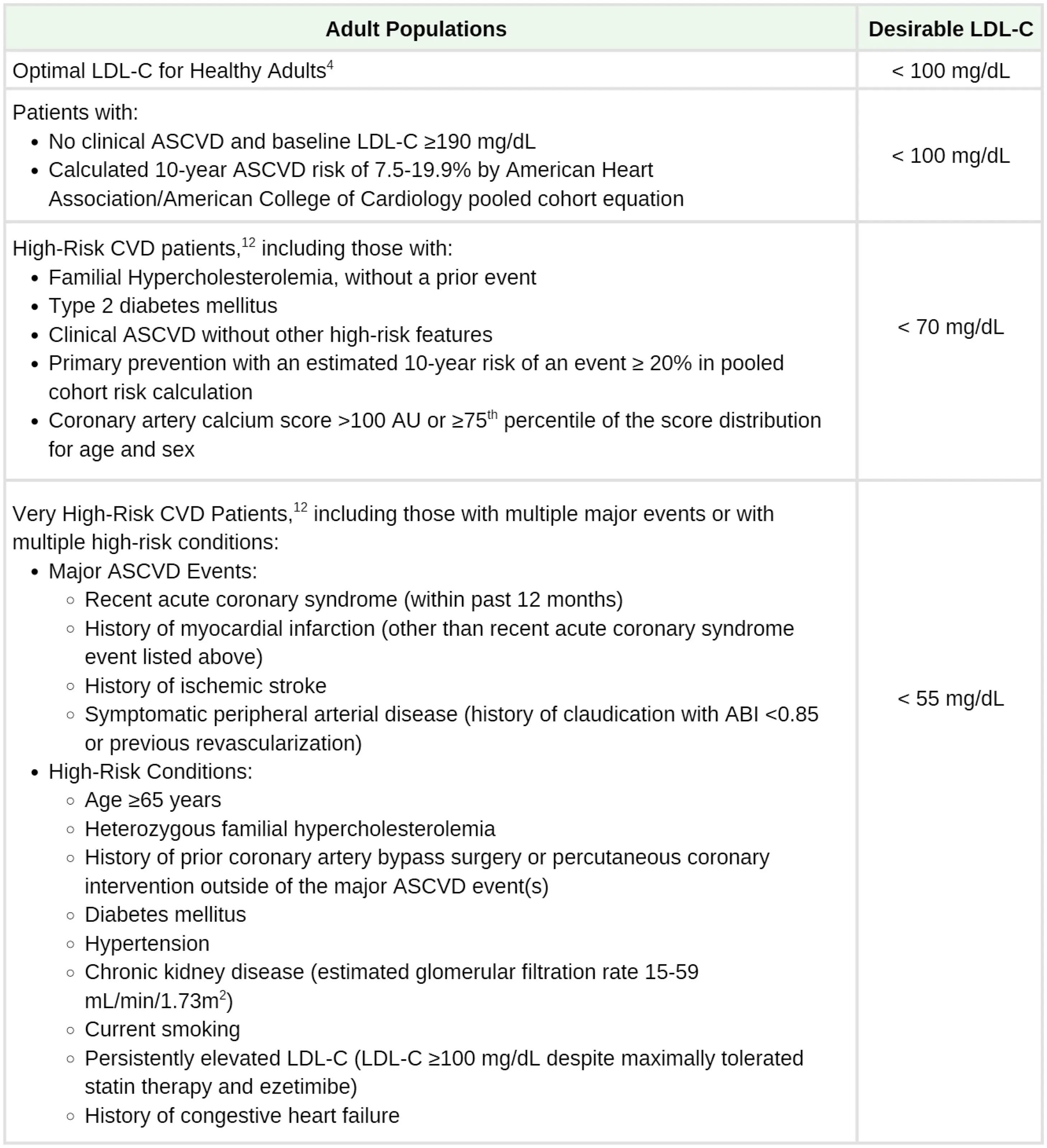 Figure source: 2
Figure source: 2
Lifestyle Modifications
- Daily physical activity
- Weight management
- Diet: reduced intake of saturated fats (to <7% of total calories), trans fatty acids (to <1% of total calories), and cholesterol (to <200 mg/d)
- Moderate- or high-intensity statin
Pharmacotherapy
- Statins
- Ezetimibe
- PCSK9 Inhibitors
- Bempedoic Acid
- Inclisiran
- Omega-3
- Fibrates
- Others
- Bile Acid Sequestrants (colestipol and colesevelam)
- Limited use due to low efficacy, significant drug interactions, pill burden
- Evinacumab
- mAb that inhibits ANGPTL3 to promote VLDL processing and clearance upstream from LDL formation.
- Monthly IV infusion administered by healthcare professional.
- Only approved for HoFH although has shown benefit for other causes of hyperlipidemia
- Robust LDL-C lowering - ~50%
- Lomitapide
- Inhibits synthesis of chylomicrons and VLDL, resulting in ↓ LDL-C
- Daily tablet only approved for HoFH.
- Robust LDL-C lowering - ~40-50%.
- Hepatotoxicity concern - requires REMS program. Significant drug interactions
- Bile Acid Sequestrants (colestipol and colesevelam)
High Intensity Statins
- Rosuvastatin 20-40 & Atorvastatin 40-80 mg
- Maximally tolerated statin still the foundation
- ↓ LDL-C ~50%
- Can get creative to identify “maximally tolerated” to manage intolerance
- Symmetric myalgias in large proximal muscle groups may indicate true statin intolerance; RARE
- SAMSON trial - 90% of muscle symptoms attributed to “nocebo effect”
- Rule out/correct other causes of muscle symptoms: hypothyroidism, vitamin D deficiency, exercise
- Hydrophilic statins potentially less muscle symptoms (rosuvastatin, pravastatin)
- Up to 90% of initially intolerant do fine with re-challenge
- Allow 2-4 week wash out
- Symmetric myalgias in large proximal muscle groups may indicate true statin intolerance; RARE
Variability in individual response to statins
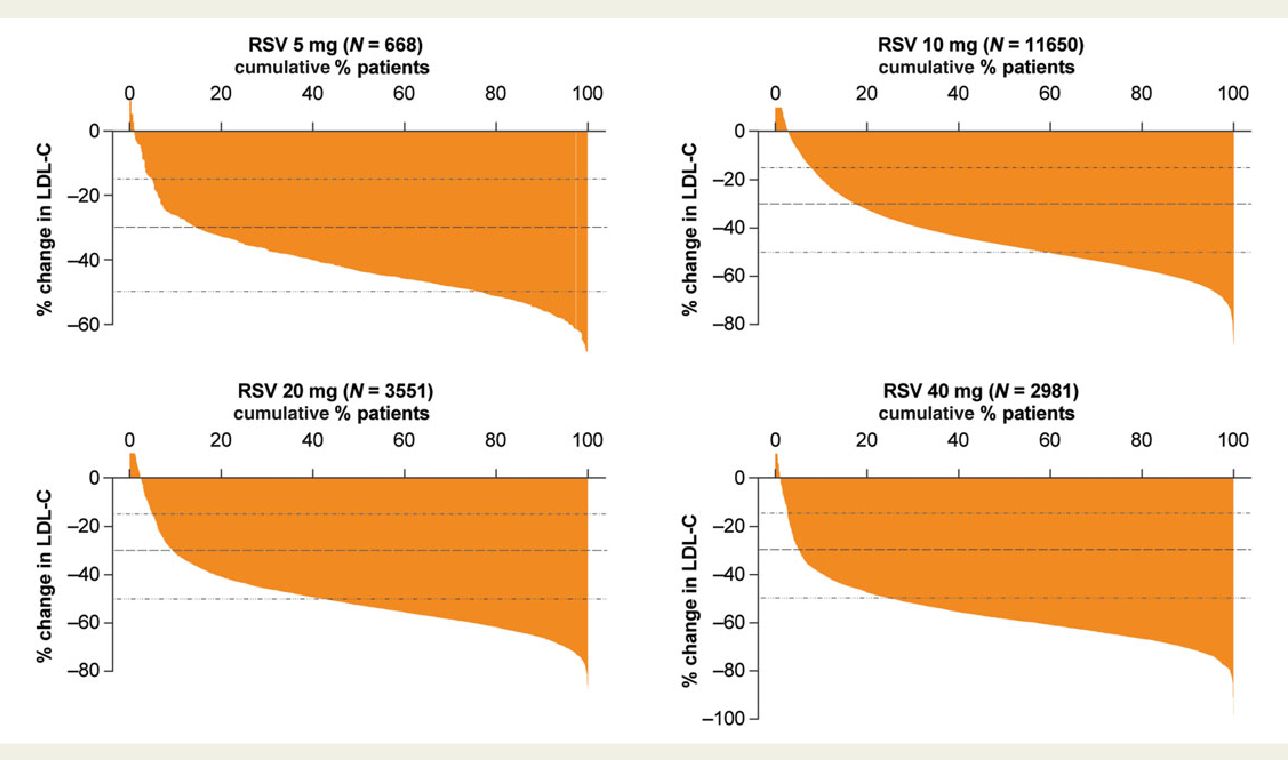
Statin-Intolerance
- Try 2-3 different daily Statins and allow a 1 mo washout between each of them
- Try less than daily statin (e.g. 1x/week, every other day, etc.)
- Start Ezetimibe
- Add PCSK9 Inhibitors if high-risk
- Add Bempedoic Acid if not high-risk
Primary Prevention
Secondary Prevention
Footnotes
-
Lloyd-Jones, D. M., Morris, P. B., Ballantyne, C. M., Birtcher, K. K., Covington, A. M., DePalma, S. M., Minissian, M. B., Orringer, C. E., Smith, S. C., Waring, A. A., & Wilkins, J. T. (2022). 2022 ACC Expert Consensus Decision Pathway on the Role of Nonstatin Therapies for LDL-Cholesterol Lowering in the Management of Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease Risk. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 80(14), 1366–1418. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2022.07.006 ↩
-
LDL Cholesterol Management Simplified in (Adults) - Lower for Longer is Better: Guidance from the National Lipid Association. Jackson, Elizabeth J. et al. ↩